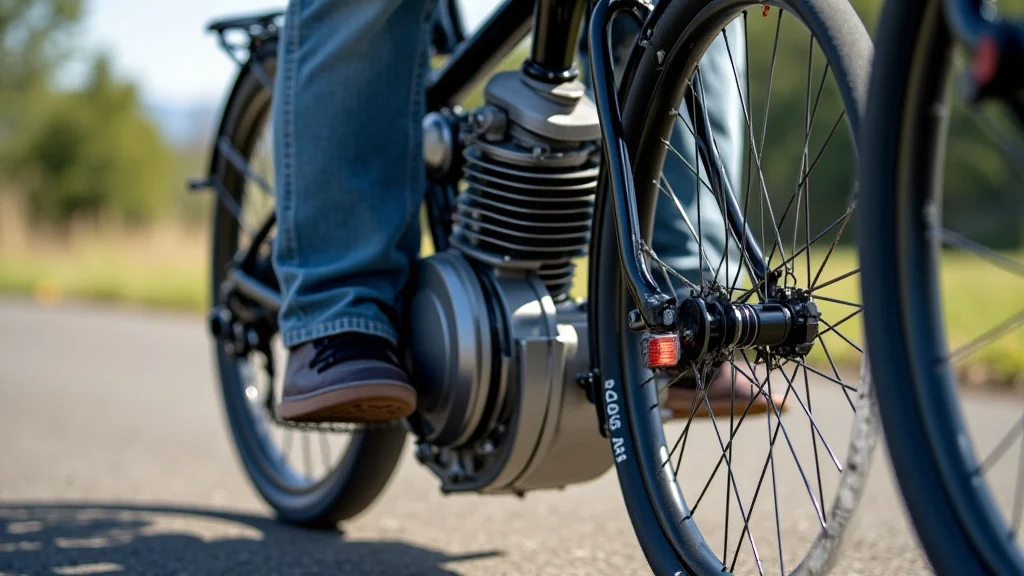
Remember that time you were riding your bike uphill, legs burning, wishing you had a little extra boost? You’re not alone! Many cyclists have daydreamed about having a powered assist, making those challenging climbs or long commutes feel effortless. The question of whether you can put a motor on a bicycle with gears isn’t just a fantasy; it’s a practical consideration for many. This post will explore everything you need to know about adding a motor to your bike, whether you have a geared system or not. You’ll learn the different motor types, the pros and cons of each, and what’s involved in the conversion process. By the end, you’ll be well-equipped to make an informed decision and potentially transform your riding experience, improving your Time on Page and reducing your Bounce Rate.
Key Takeaways
- Discover the different types of motors suitable for bicycle conversions, including their advantages and disadvantages.
- Understand how geared bicycles interact with electric motor systems.
- Learn about the key components involved in a successful motorization project.
- Explore the legal and safety considerations associated with adding a motor to your bicycle.
- Gain insight into the performance changes and potential benefits of an electric bicycle conversion.
- Find out the factors influencing the cost of adding a motor and how to budget appropriately.
Getting Started: Exploring Bicycle Motorization Options
The prospect of adding a motor to your bicycle opens a whole new world of possibilities, from easier commutes to longer recreational rides. However, before you jump in, it’s key to explore the different routes you can take. This starts with choosing the right motor type and understanding how it will interact with your existing bicycle components, especially the gears. There’s a lot to consider: the power output, the type of terrain you ride on, your budget, and the level of technical skill involved in the conversion. It’s also important to familiarize yourself with any local regulations regarding electric bicycles to ensure you are compliant.
Motor Types: What’s Available?
Choosing the right motor is the first, and possibly most important, decision. Several motor types are available for bicycle conversion, each with unique characteristics and performance benefits. Selecting the right motor depends on your specific needs, the type of riding you do, and your budget. Selecting the right motor will dramatically impact your riding experience.
- Hub Motors: These motors are built directly into the wheel hub (front or rear).
Hub motors are known for their simplicity and ease of installation, often making them a popular choice for beginners. Installation usually involves removing the original wheel and replacing it with the motorized wheel, along with connecting the battery and controller. They come in both geared and direct-drive configurations. Geared hub motors offer better torque, making them excellent for climbing hills, while direct-drive motors can provide higher top speeds. Hub motors are typically less expensive to install compared to mid-drive options.
- Mid-Drive Motors: These motors are positioned in the center of the bicycle frame, where the pedals are.
Mid-drive motors are known for their efficiency and often better weight distribution, leading to a more natural riding feel. They connect to the bicycle’s chain, utilizing the existing gears to optimize power delivery. This allows riders to take advantage of the full range of gears, providing more versatility in varying terrains. Mid-drive systems generally offer more power and torque than hub motors. The conversion may be more complex, often requiring specialized tools and a higher skill level. These systems are usually more expensive than hub motors.
- Friction Drive Motors: These motors use a roller that presses against the tire to propel the bike.
Friction drive systems are typically the least expensive and easiest to install. They are often sold as kits that clamp onto the frame. Their simplicity is appealing, but they have some notable drawbacks. They can be less efficient than hub or mid-drive motors and may struggle in wet conditions, where the roller can slip against the tire. They may also cause increased tire wear. Friction drive motors are usually the least powerful option.
Compatibility with Geared Bicycles
The good news is that most electric motor systems are compatible with bicycles that have gears. The motor type you choose will largely determine how those gears function with the system. Understanding this interplay is key to maximizing performance and enjoyment. Not all motors integrate in the same way, so it’s essential to understand the differences.
- Hub Motors and Gears: Hub motors often work independently of the gears, at least directly.
Typically, the electric motor’s power is delivered directly to the wheel, and the rider’s pedaling action and the bicycle’s gears provide additional assistance or efficiency. The rider can choose to use the gears to make pedaling easier, especially at higher speeds or on inclines. Geared hub motors are designed to provide added torque for climbing hills. In essence, the gears allow you to optimize your pedaling effort.
- Mid-Drive Motors and Gears: Mid-drive motors are designed to use the bicycle’s gears.
This direct integration offers significant advantages. The motor’s power is delivered to the chain, just like your pedaling power. This means the rider can leverage the full range of gears to climb hills, increase top speed, or maximize efficiency. This setup offers the most natural feel and allows for optimized power delivery in various riding conditions. This is often seen as the superior setup.
- Friction Drive Motors and Gears: Friction drive motors tend to be less dependent on your gears.
Because they connect to the tire, they do not directly interact with the gears. However, the rider can still use their gears to make pedaling more efficient or to control their speed and effort. The friction drive motor provides power to the wheel, while the gears provide the option for the rider to adjust their physical effort. In practice, the use of gears is still useful for maintaining a comfortable cadence and optimizing the use of battery power.
Essential Components for Conversion
Adding a motor to your bicycle isn’t just about slapping on a motor and calling it a day. Several key components work together to convert your standard bicycle into an electric one. Understanding these elements is essential for a successful conversion, and can influence the performance and overall cost of the project. Each component plays a vital role in providing power, control, and efficiency. Some of the components vary depending on the system you choose.
Power Source: Batteries
The battery is the heart of any electric bicycle system, storing the energy that drives the motor. The type and capacity of the battery significantly influence range, performance, and overall cost. A good quality battery is essential for a satisfying riding experience. Investing in a reliable battery is critical to avoid frustration and ensure safety.
- Battery Type: Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries are the most common choice.
Li-ion batteries are favored for their high energy density, lightweight design, and long lifespan. They’re a significant improvement over older battery technologies, such as lead-acid. Li-ion batteries come in various configurations, including those designed to be mounted on the frame or integrated into the bike’s design. The choice of battery type influences factors like range and weight.
- Battery Capacity: Battery capacity, measured in Watt-hours (Wh), determines how far you can travel.
A higher Wh rating means a longer range. Battery capacity is calculated by multiplying the voltage (V) of the battery by its amp-hour (Ah) rating. For example, a 36V 10Ah battery has a capacity of 360 Wh. The range can vary depending on riding conditions, rider weight, and how much assistance the motor provides. Riders who plan longer trips should choose batteries with higher capacity.
- Battery Management System (BMS): This built-in system protects the battery.
The BMS regulates the charging and discharging of the battery cells, preventing overcharging, over-discharging, and short circuits. This system is key for battery lifespan and rider safety. It also monitors the battery’s temperature and performance, providing important data to the rider. A well-designed BMS is essential for the long-term health and safe operation of the battery.
Motor Controller
The motor controller is the “brain” of the electric bicycle system. It regulates the flow of power from the battery to the motor, managing speed, torque, and efficiency. The controller is one of the more important components, playing a key role in the overall performance of the e-bike.
- Controller Functions: Controllers manage motor speed, torque, and power delivery.
They take signals from the throttle or pedal-assist system (PAS) to adjust the motor’s output. The controller also protects the motor and battery by monitoring voltage and current levels. Modern controllers often include features like regenerative braking, which can recover energy when braking to recharge the battery. High-quality controllers offer a smooth and responsive riding experience.
- Types of Controllers: Controllers vary based on their voltage and current ratings.
The voltage of the controller must match the voltage of the battery. The current rating determines the maximum power the motor can draw. Selecting the correct controller is critical for the motor’s performance and safety. Controllers can also have different modes like eco and sport, allowing riders to adjust the level of assistance.
- Controller Settings: Many controllers allow for customization.
Riders can often adjust settings such as speed limits, acceleration rates, and power levels. Some controllers are programmable via a computer connection, offering advanced control options. These adjustments allow riders to personalize their riding experience. These settings can greatly enhance the performance of the bike.
Throttle and Pedal Assist System (PAS)
The throttle and PAS are the interfaces that the rider uses to control the motor. These systems determine how the motor’s power is applied, offering the rider various options for assistance. They significantly influence the riding experience.
- Throttle Control: A throttle, often a twist-grip or thumb throttle, provides on-demand power.
The throttle allows the rider to control the motor’s output directly. Twist throttles are similar to motorcycle throttles, while thumb throttles are often found on scooters. The rider can choose to use the throttle for full power, partial assistance, or not at all. Throttle control is popular for its simplicity and immediate response.
- Pedal Assist System (PAS): PAS provides assistance as you pedal.
PAS systems use a sensor to detect when the rider is pedaling and provide assistance proportional to the pedal input. PAS offers a more natural riding experience, with the motor kicking in as you pedal. Different levels of assistance are usually available, allowing the rider to adjust the motor’s output to their preference. PAS can significantly extend the battery range.
- Combined Systems: Many e-bike systems offer both throttle and PAS.
This gives the rider the flexibility to choose the assistance method that best suits their needs. Riders can use the throttle for quick bursts of power or to overcome difficult sections. PAS is ideal for longer rides, providing a smooth and efficient way to travel. The combination offers maximum riding flexibility and control.
Other Crucial Components
Beyond the core components, some other pieces play a vital role. These elements help ensure safe and effective operation. They can impact the reliability and durability of the system.
- Display Unit: The display unit provides real-time information.
The display shows speed, battery level, assist level, and other data. It is often mounted on the handlebars, allowing riders to monitor performance while riding. More advanced displays may include GPS functionality, trip computers, and connectivity features.
- Wiring Harness: This provides electrical connections.
The wiring harness is responsible for connecting all components, ensuring they communicate effectively. High-quality wiring and connectors are essential for system reliability and safety. Proper routing and protection of the wiring harness are necessary to prevent damage.
- Brakes and Sensors: Brake sensors ensure safety.
Brake sensors cut off the motor when the brakes are applied, preventing unwanted acceleration. These sensors are integrated into the brake levers or calipers. Upgrading your brakes might be necessary to handle the increased weight and speed of an e-bike. They are a necessary safety element.
Legal and Safety Considerations: Before You Ride
Before you can put a motor on a bicycle with gears and start zipping around, it’s essential to understand the legal and safety considerations. Regulations vary by location, and they dictate what is permissible. Safety should be a top priority at every step of the process.
Regulations and Compliance
Local regulations vary, and you are responsible for making sure you follow them. These rules often define the motor power, speed limits, and whether the bicycle needs to be registered. Ignoring them can lead to fines, confiscation of your bike, and even legal problems.
- E-Bike Classification: Know your local e-bike classifications.
Many areas categorize e-bikes into classes based on their motor power and top speed. Class 1 e-bikes, for example, often have pedal-assist motors with a maximum speed of 20 mph. Understanding these classifications will help you make decisions about what components you can use and how your e-bike can be used.
- Power and Speed Limits: Be aware of power and speed restrictions.
Most jurisdictions set limits on the motor’s power output (measured in watts) and the maximum speed at which the motor can assist the rider. These limits are designed to balance the benefits of e-bikes with safety concerns. Overstepping these limits can lead to legal issues.
- Registration and Licensing: Some areas require registration and/or licensing.
Some e-bikes require registration with local authorities and may require the rider to obtain a driver’s license. The rules vary, so you must research the regulations. This is similar to the requirements for motorcycles. Failure to follow these rules could result in penalties.
Safety Guidelines and Best Practices
Riding an electric bicycle presents new responsibilities, and the first step is to prioritize your safety. Following safe riding practices is critical for yourself and others.
- Helmet Use: Always wear a properly fitted helmet.
A helmet is the most important piece of safety gear. It protects your head in the event of a crash. Make sure your helmet fits correctly and is properly fastened. It is a good idea to refresh your memory on the latest guidelines for helmet fitting.
- Braking and Handling: Practice your braking and handling skills.
E-bikes are heavier and can travel faster than regular bicycles, affecting braking distances and handling. Practice stopping and making turns in a safe, controlled environment. Practice in an area without traffic before riding on roads.
- Traffic Awareness: Stay aware of traffic and follow traffic laws.
Obey all traffic laws, signals, and signs. Use hand signals when turning. Be visible to other road users, especially at night. Ride defensively and be prepared for unexpected actions by cars, pedestrians, or other cyclists.
Performance and Benefits: What to Expect
Adding a motor to your bicycle fundamentally changes how you ride. The motor gives you a boost, but there are other benefits. You may experience a new riding experience that can be both more enjoyable and more practical. The type of motor impacts how the bike performs.
Enhanced Riding Experience
The most immediate and obvious benefit of motorizing your bicycle is the enhanced riding experience. That uphill struggle, the long commutes, and the resistance from the wind will all be easier. This helps make riding more fun.
- Easier Hill Climbing: Motors make hills less challenging.
One of the most appealing features is the ability to tackle hills with ease. The motor assists the rider, reducing the physical effort required to climb steep inclines. This is particularly advantageous for riders living in hilly areas or those who often encounter uphill routes.
- Extended Range: Electric assistance allows for longer rides.
With an e-bike, you can travel further on a single charge. The electric motor helps to conserve your energy, allowing you to ride for extended periods. This makes it a great choice for long commutes, recreational cycling, or exploring new routes that are normally too long.
- Reduced Physical Strain: Less physical effort means less fatigue.
The motor takes over some of the work, reducing the physical strain on the rider. This makes riding more accessible to people of all fitness levels. This feature is particularly helpful for those with joint problems or other physical limitations that make traditional cycling challenging. This will keep you fresher for a longer time.
Practical Advantages
Beyond the enhanced riding experience, motorized bicycles offer other practical advantages, making them a great tool for a variety of tasks.
- Commuting Efficiency: E-bikes can make commuting faster.
Electric bikes are great for commuting and can reduce travel time. The motor helps riders travel at higher speeds. This can mean avoiding traffic jams, and even reaching the destination faster than by car. Additionally, e-bikes can be a great alternative to public transit.
- Environmental Benefits: E-bikes are an eco-friendly transport option.
E-bikes produce zero emissions, making them a more eco-friendly transportation option. They replace the use of cars, reducing your carbon footprint. This is a very compelling reason to switch from your old bike or even a car.
- Increased Cargo Capacity: Adding a motor does not mean a loss of functionality.
E-bikes can still be equipped with racks and panniers, increasing the carrying capacity. This means you can use your e-bike for carrying groceries, supplies, or other items. This can be great for running errands and helps replace a car for short trips.
Performance Metrics and Considerations
The performance of your electric bicycle depends on various metrics. It is also impacted by the choice of motor, battery, and controller. Paying attention to these metrics helps you optimize the performance of your electric bicycle.
- Speed and Acceleration: The top speed depends on the motor and local regulations.
Electric bikes offer significantly increased speed and acceleration compared to traditional bicycles. The top speed is often limited by law. Acceleration depends on motor power and the controller settings. A more powerful motor gives quicker acceleration, making it easier to start from a standstill and merge with traffic.
- Range: The range depends on several factors.
The range of your e-bike, or how far you can travel on a single charge, depends on the battery capacity, the terrain, the rider’s weight, and the level of assistance. A larger battery, flat roads, and using a lower assist setting will all increase your range. The average range can vary from 20 to 80 miles.
- Torque: Torque affects the power for hills and acceleration.
Torque, measured in Newton-meters (Nm), indicates the motor’s rotational force. Higher torque makes it easier to climb hills and accelerate quickly from a standstill. Mid-drive motors often provide more torque. It impacts your overall riding performance.
According to a report by the Electric Bike Worldwide Report, the global e-bike market is projected to reach $80.6 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 11.2% from 2020 to 2027.
Cost Considerations: Budgeting for Your Conversion
The cost of adding a motor to a bicycle is an important consideration. The overall expense can vary, depending on several factors. Budgeting is important to ensure you get the features you want. Knowing what influences the cost will help you make decisions.
Components and Kits
The most important factor in the cost is the type and quality of the components. The choices that are made in these areas can dramatically affect the total price.
- Motor Type: Hub motors are often the most affordable.
Hub motors tend to be the most affordable option. This makes them a great option for those new to electric bikes or wanting to keep expenses low. They typically offer a solid balance of performance and price. The cost of a hub motor kit can range from $300 to $800.
- Battery Quality: Batteries are a major expense.
Batteries are one of the most significant expenses. The cost varies based on the battery capacity, the technology used, and the quality of the cells. High-quality Li-ion batteries with a longer lifespan will cost more than budget options. Expect to spend from $200 to $1000 or more on a battery.
- Kit vs. Custom Build: Kits are more cost-effective.
Buying a complete conversion kit is often more cost-effective. They come with everything you need, including the motor, battery, controller, display, and wiring. This also helps with the selection of components. Building a custom system lets you choose each component individually. This often results in higher costs, but provides greater flexibility in terms of the components and the motor.
Installation and Labor
Whether you choose to do the conversion yourself or hire a professional will also affect the final cost. Installation can be straightforward or complex, depending on the motor type and the bicycle model.
- DIY vs. Professional Installation: Self-installation saves on labor.
If you have some mechanical skill, you can save money by installing the motor kit yourself. This is a good option if you are comfortable working with tools and following instructions. If you lack experience or are not comfortable with mechanical work, hiring a professional will add to the total cost. Expect to pay between $100 and $500 for professional installation.
- Tools and Expertise: The need for specialized tools can add costs.
Depending on the type of motor, the conversion may require specialized tools. The use of these tools can add to the overall cost if you are doing it yourself. Mid-drive systems, for instance, may require a bottom bracket removal tool. Professional installers have these tools and expertise. This is also something to consider.
- Upgrades and Modifications: Additional parts can increase the cost.
You may also need to upgrade other components, such as brakes or tires, to handle the increased weight and speed of an e-bike. These upgrades add to the overall cost. The need for these upgrades depends on the condition of your existing components and the performance needs of the new e-bike. Upgrades will impact the final cost.
Long-Term Expenses
Once you can put a motor on a bicycle with gears and complete the project, there are ongoing costs. These costs should be part of the decision-making process. The expenses are important when planning for the long term.
- Battery Replacement: Batteries degrade over time.
Batteries have a limited lifespan and will eventually need to be replaced. The lifespan of a Li-ion battery typically depends on usage, charging practices, and storage conditions. Expect to replace the battery every few years. The replacement cost will depend on battery capacity and technology.
- Maintenance and Repairs: Motors and components may need servicing.
Electric bike systems require occasional maintenance and may need repairs. This can include replacing worn components, checking the wiring, or servicing the motor. The need for repairs will depend on the frequency of use, the quality of the components, and the conditions in which the bike is used. These costs should be considered in the overall budget.
- Running Costs: Consider electricity costs.
The cost of electricity to charge your e-bike is minimal compared to the cost of gasoline. However, it is an ongoing expense. These costs are very low. The running costs for an e-bike are usually much lower than the expenses for a car.
According to a study by the Transportation Research Board, the average operating cost of an electric bicycle is approximately $0.01 per mile, compared to $0.10 to $0.15 per mile for a gasoline-powered car.
Common Myths Debunked
There are several common myths associated with adding a motor to a bicycle. It is important to know fact from fiction, allowing you to make well-informed decisions.
Myth 1: E-bikes are cheating.
The reality is that e-bikes offer a boost, but they still require physical effort from the rider, especially in pedal-assist mode. Electric bikes allow cyclists of varying fitness levels to enjoy the benefits of cycling, such as exercise and access to outdoors. Many e-bike users still experience health benefits, such as improved cardiovascular health, similar to those gained from conventional cycling. It is more accurately described as “assisted cycling,” which can encourage more people to ride.
Myth 2: Electric bikes are unsafe.
The truth is that e-bikes, like traditional bicycles, can be safe when used responsibly. Modern e-bikes come with safety features, such as disc brakes, regenerative braking, and integrated lights. Proper safety measures include following traffic rules, wearing a helmet, and practicing safe riding skills. Regular maintenance and inspection of the e-bike components are essential for safety.
Myth 3: Electric bikes are only for older people.
The reality is that e-bikes are a great choice for people of all ages and fitness levels. E-bikes offer the ability to experience the joy of cycling, regardless of age. They provide benefits such as a shorter commute or the ability to experience a hill or mountain more easily. E-bikes enable older adults to stay active. E-bikes are used by commuters, recreational cyclists, and everyone in between.
Myth 4: E-bikes are too expensive.
While the initial cost of an e-bike may be higher than a regular bike, there are numerous economic benefits. E-bikes offer long-term cost savings compared to car ownership, including lower fuel and maintenance costs. The upfront cost can be spread over many years. When you consider the savings on gasoline, parking, and maintenance, e-bikes can provide great value for money. They can also provide savings on car use.
Myth 5: E-bikes are difficult to maintain.
The truth is that e-bikes are not difficult to maintain if you perform regular maintenance. Modern e-bikes are built to withstand everyday use. Maintenance tasks are the same as with a conventional bicycle, with an emphasis on lubrication, tire pressure, and brake adjustments. You should regularly check the motor, battery, and controller components. Many professional bike shops can service e-bikes.
Frequently Asked Questions
Question: What is the top speed of an e-bike?
Answer: The top speed is typically limited by regulations. In many areas, the motor can assist up to 20 mph or 28 mph.
Question: How far can an e-bike go on a single charge?
Answer: The range varies based on battery capacity, terrain, and riding style, but it typically ranges from 20 to 80 miles.
Question: How long does it take to charge an e-bike battery?
Answer: Charging times vary, but most batteries charge fully in 2 to 6 hours.
Question: What kind of maintenance does an e-bike require?
Answer: E-bikes require basic maintenance such as lubricating the chain, checking tire pressure, and ensuring brakes function.
Question: Is it possible to convert any bike into an e-bike?
Answer: Most bicycles are capable of being converted, but some may need modifications to accommodate the motor and battery.
Final Thoughts
So, can you put a motor on a bicycle with gears? Absolutely! As you’ve seen, it opens up a world of possibilities, making cycling more accessible, enjoyable, and efficient. From hub motors to mid-drive systems, the options available provide something for every rider and every budget. Now you have the information to explore the various motor options, understand the importance of essential components, and grasp the legal and safety guidelines you must follow. You have discovered the potential benefits of this, and the costs involved. With this knowledge, you are in a great position to make an informed decision on whether to electrify your ride. Consider the type of riding you do, the terrain you’ll cover, and your budget. By taking the time to research and understand the process, you can transform your bicycle into a reliable, efficient, and fun mode of transportation. Whether it’s to conquer those hills, extend your rides, or commute more efficiently, the world of electric bikes awaits. Start exploring, and get ready to enjoy the ride!